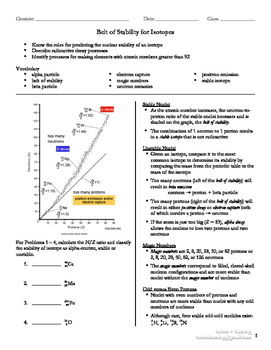
39 band of stability worksheet
gray area is called the band of stability. Instructions: Locate where the following atoms would be on the graph below. Pay careful attention to your calculations. Label each atom after it has been plotted. Note: Potassium-41 has been plotted for you. 81 35 238 92 191 77 24 12 60 195 77 200 180 Band of stability 160 140 aaaaaasa 120 aaaaaaa ...
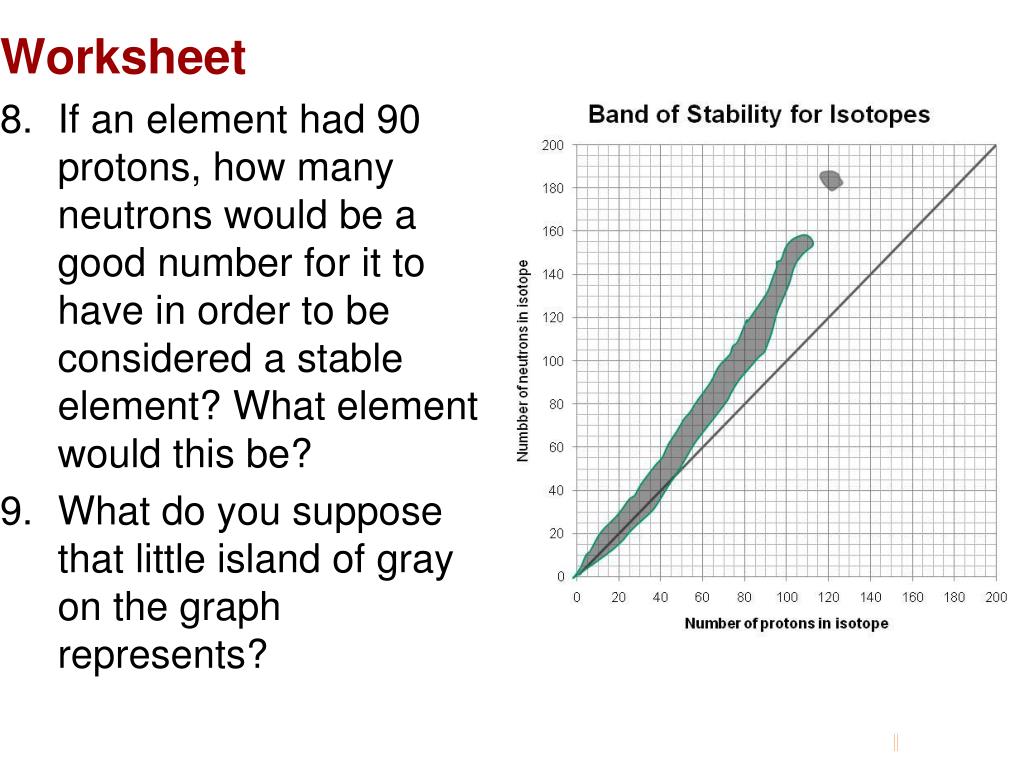
6. Nuclides below the band of stability in the figure 1 have a N / Z ratio which is too low. Using your answer to question 3, which of the 6 modes of decay might such a nuclide undergo to approach the band of stability? Fill in your answer in the box on the figure overleaf. 7. Nuclides with Z > 83 are beyond the band of stability and are ...
Radioactivity and Nuclear Physics Worksheets. admin June 13, 2019. Some of the worksheets below are Radioactivity and Nuclear Physics Worksheets, Basic Principles of Nuclear Physics : Nomenclature and common units, The realm of atomic and nuclear physics, The chart of the nuclides or Segre Chart, Isotope, Isobar, Isotone, ….

Band of stability worksheet
Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet Fluorine-18 decays to oxygen-18 by positron emission. Sodium-24 decays by beta emission. Krypton-76 absorbs a beta particle to form bromine-76. Aluminum-27 absorbs an alpha particle to form phosphorus-30 and emits a neutron. 30 Nitrogen-14 absorbs an alpha particle to form oxygen-17 and emits a proton.
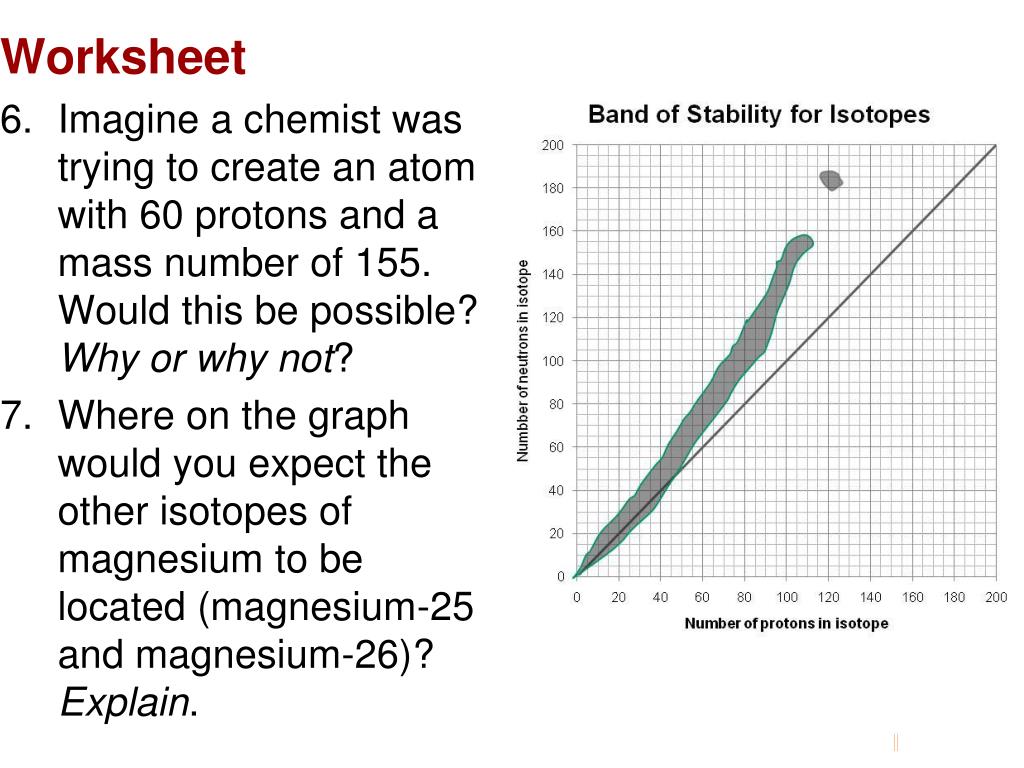
Name:_____ Per:_____ Worksheet- Band of Stability Objective: Determine if an atom is "stable", "unstable (aka radioactive)", or "does not exist" based on its position on the graph below. Background Info: Isotopes of elements found in nature are all located within the gray area on the graph below called the band of stability.
Band of Stability Worksheet.pdf - Google Docs ... Loading…
Band of stability worksheet.
decay series, band of stability The atomic nucleus and radioactivity, kinetics of radioactive decay Alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, alpha decay, beta decay Nuclear fusion, nuclear fission, nuclear strong force Chemical applications, biological effects of radiation Alpha Decay Nuclear equations, half-
Name:_____ Per:_____ Worksheet- Band of Stability Objective: Dete rmine if an atom is "stable", "unstable (aka radioactive)", or "does not exist" based on its position on the graph below. Background Info : Isotopes of elements found in nature are all located within the gray area on the graph below called the band of stability .
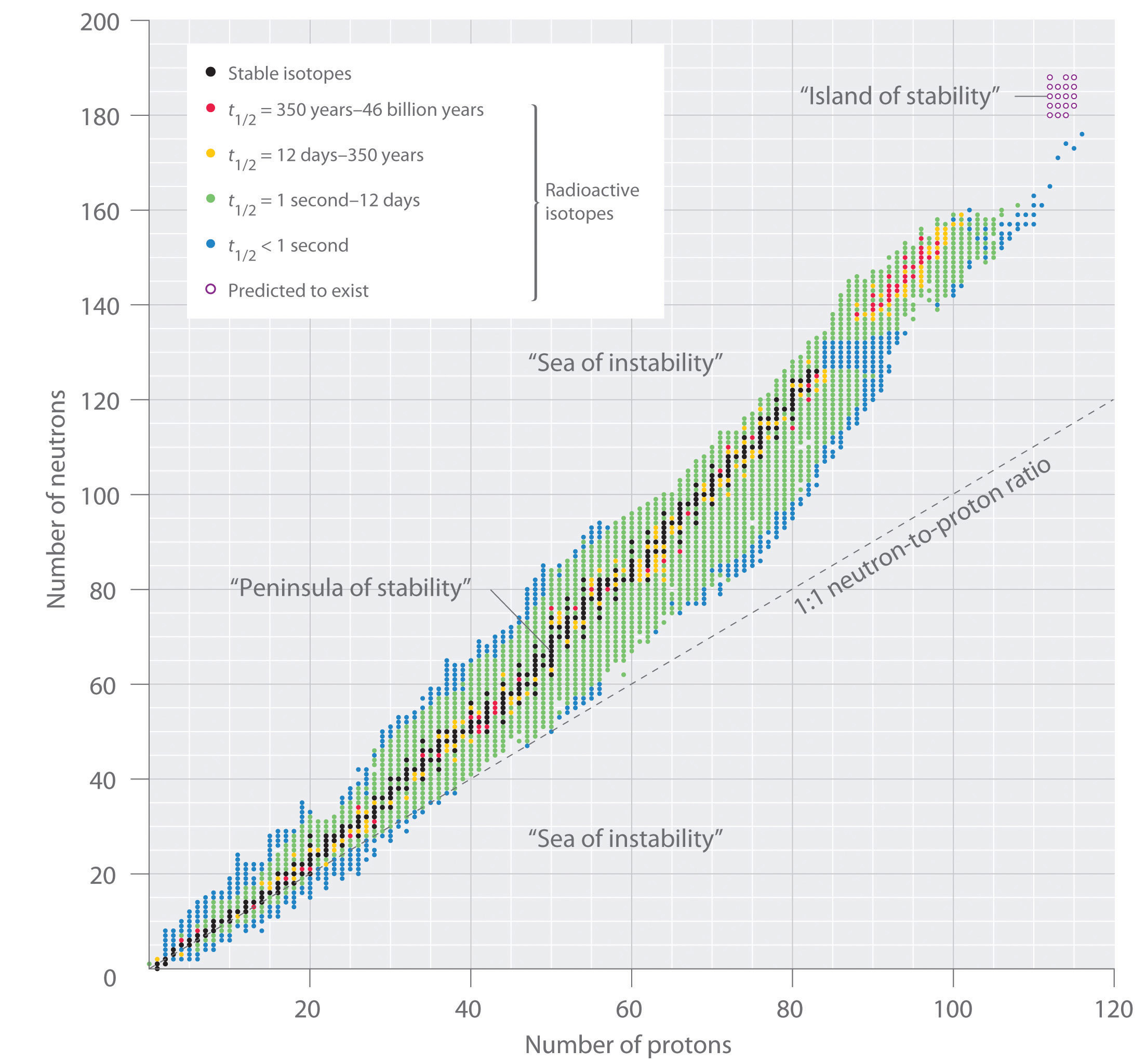
The band of stability also includes radionuclides because smooth lines cannot be drawn to exclude them. The band of stability also stops at element 83 because there are no known stable isotopes above it. Elements lying outside the band of stability would be too unstable to justify the time and money for an attempt to make it.
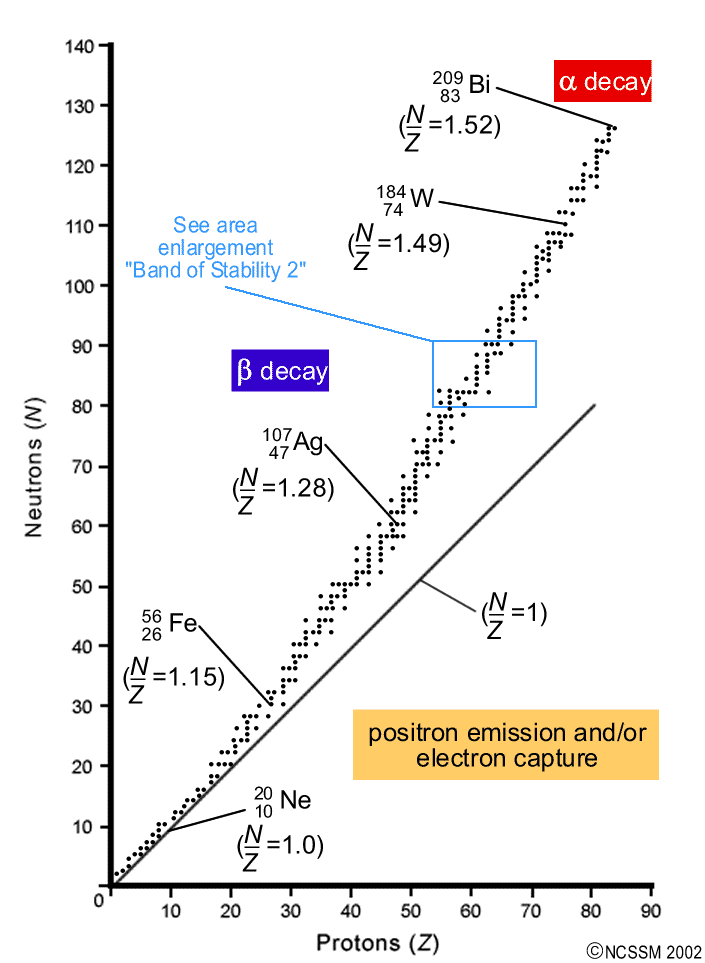
Unstable atoms gain stability by emitting radiation. The stability of an atom's nucleus can be correlated with its neutron-to-proton (n/p) ratio. Stable nuclei of atoms with low atomic numbers (X 20) have a n/p ratio of 1:1. For larger nuclei, the n/p ratio is closer to 1.5:1. Stable nuclei are found in an area called the Band of Stability.
The graph of stable elements is commonly referred to as the Band (or Belt) of Stability. The graph consists of a y-axis labeled neutrons, an x-axis labeled protons, and a nuclei. At the higher end (upper right) of the band of stability lies the radionuclides that decay via alpha decay, below is positron emission or electron capture, above is ...
*Worksheet- Band of Stability (Front) /2 6. * Worksheet- Nuclear Decay (back) /2 7. *Worksheet- ½ Life and Radioactive Decay (front) /2 8. *Worksheet- Activity Radioactive dating (back) /2 9. *Worksheet- Nuclear Reactions /2 10. Notes- Atomic Structure & Nuclear. chem. /2 ...
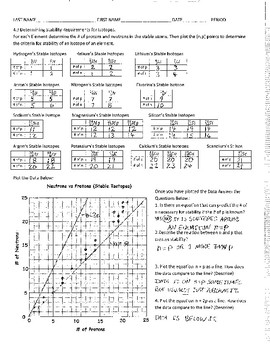
Part 1 - Create a "Band of Stability" You will be graphing the proton and neutron numbers for some isotopes that are known to be stable. 1. Using an entire side of a piece of graph paper, draw a vertical "y" axis and label it "Neutrons." Draw a horizontal "x" axis and label it "Protons". (1 point each) 2.
Band of Stability Lab worksheet. advertisement BAND OF STABILITY LAB INTRODUCTION: Most elements have isotopes. For stable isotopes, an interesting plot arises when the number of neutrons is plotted versus the number of protons. Because the plot shows only the stable isotopes, this graph is often called the Nuclear Belt of Stability. ...
Worksheet band of stability Author: Kiziva Piyoyewudu Subject: Worksheet band of stability. Stable nuclides, if located on a graph of several protons versus a number of neutroons, all fall in Created Date: 3/10/2020 1:21:17 PM
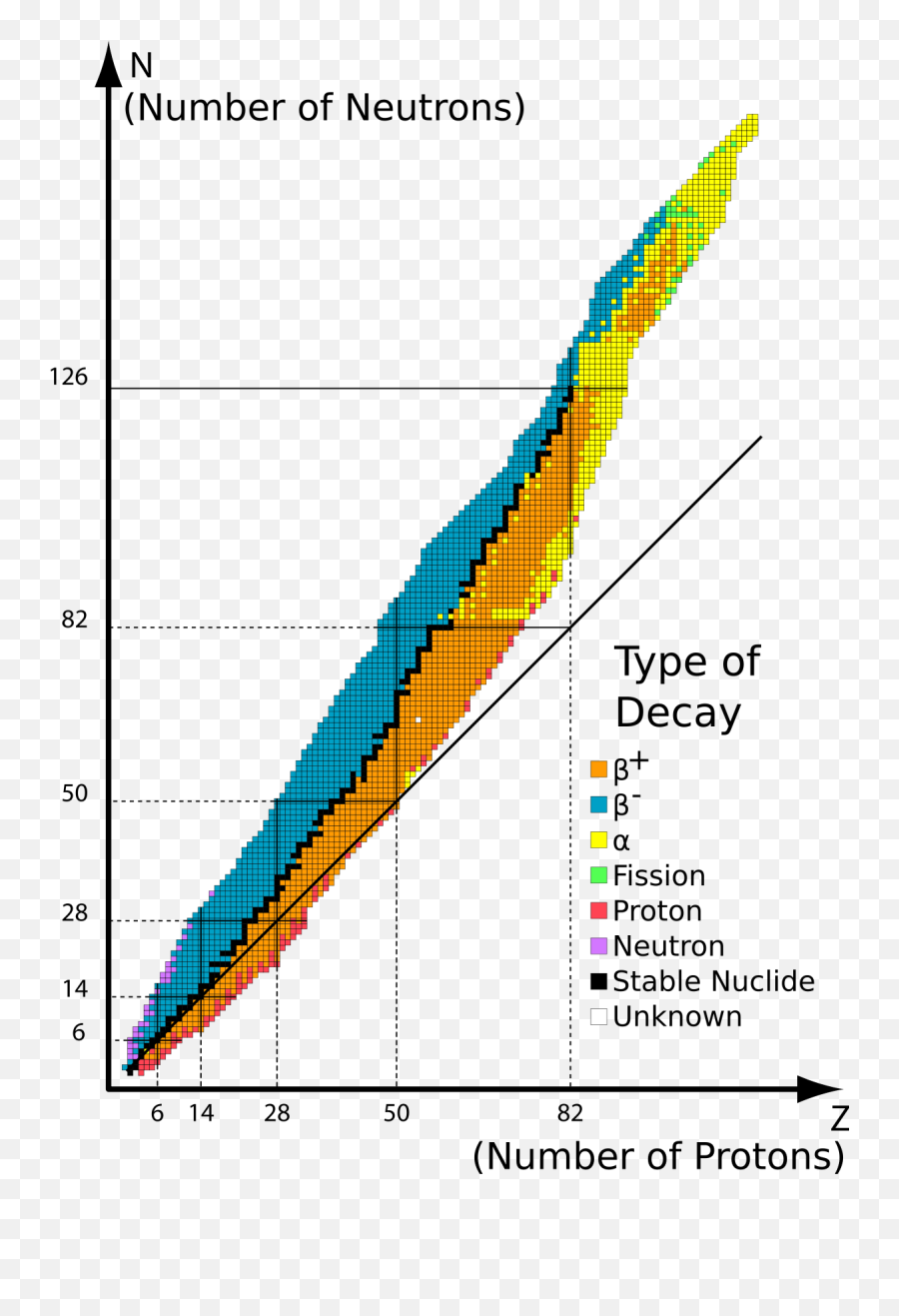
This region is known as the band of stability (also called the belt, zone, or valley of stability). The straight line in Figure 1 represents nuclei that have a 1:1 ratio of protons to neutrons (n:p ratio). Note that the lighter stable nuclei, in general, have equal numbers of protons and neutrons. For example, nitrogen-14 has seven protons and ...
Chemistry Graphs: The Band of Stability. Most elements have isotopes. For stable isotopes, an interesting plot arises when the number of neutrons is plotted versus the number of protons. Because the plot shows only the stable isotopes, this graph is often called the Nuclear Belt of Stability.
Nuclei below the belt of stability (low neutron-to-proton ratios) either emit positrons or capture electrons (one more neutron, one less proton!). Nuclei with Z > 83 tend to undergo -decay (loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons; gets smaller fast!) Some radioactive nuclei must undergo multiple steps to reach the belt of stability.
Year 7 Cells Worksheet, Year 2 Maths Mentals Worksheets, Connectives Worksheet Year 7, Year 2 Maths Worksheets Nz, Conjunctions Worksheet Year 7, Year 2 Maths Worksheets Nsw, Year 7 Chromatography Worksheet, Year 2 Maths Number Worksheets, Commas Worksheet Year 7, Year 2 Maths Worksheets Online, Crusades Worksheet Year 7, Year 2 Maths ...
The band of stability allows us to determine which isotopes of a particular element are stable and which isotopes are unstable. If an atom has the same number of neutrons as it does protons, will it be an isotope found in nature?
There is a "belt" or "band" of stability (zone with stable nuclei) Above the band of stability: o too many neutrons o expect β particle radiation 1 0n ! 1 1p+ 0 1 14 6C ! 14 7N+ 0 1 Below the band of stability o too many protons o expect positron radiation or electron capture 1 1p ! 1 0n+ 0 +1 38 19K ! 38 18Ar+ 0 +1 1 1p+ 0 1e ! 1 0n 37
Name:_____ Per:_____ Worksheet- Band of Stability Objective: Dete rmine if an atom is "stable", "unstable (aka radioactive)", or "does not exist" based on its position on the graph below. Background Info: Isotopes of elements found in nature are all located within the gray area on the graph below called the band of stability.
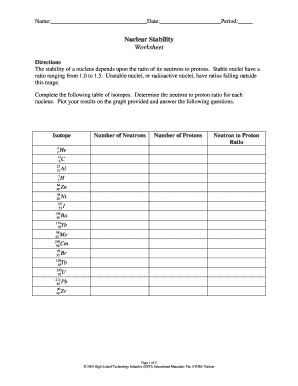
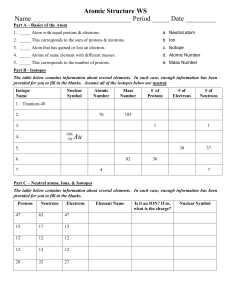
Nuclear Stability Worksheet Key Directions The stability of a nucleus depends upon the ratio of its neutrons to protons. Stable nuclei have a ratio ranging from 1.0 to 1.5. Unstable nuclei, or radioactive nuclei, have ratios falling outside this range. Complete the following table of isotopes. Determine the neutron to proton ratio for each nucleus.
Valley of Stability. Whenever the difference between neutrons to protons within a nucleus is significant enough an isotope is radioactive. Concept #1: The central idea of nuclear chemistry is that unstable nuclei will give off radiation. Concept #1: The central idea of nuclear chemistry is that unstable nuclei will give off radiation.
Atomic Stability Worksheet-Teacher Answer Key 1. Create a pretend radioactive nucleus for Element 1 including 5 neutrons (N) and 6 protons (P). Element1 N: 5 P: 6 2. Demonstrate what happens toElement 1 when the pretend radioactive nucleus emits an alpha particle and a new element (Element2) is formed.
Band of Stability. Certain isotopes are more stable than others. Their stability is determined by the ratio of the number of neutrons to the number of protons in the nucleus. At low atomic masses, the stable ratio is approximately 1:1. At about an atomic mass number of 20 this starts to increase until it is around 1.5:1 for the very heavy elements.
One of the ways that nuclides with more than 83 protons change to reach the band of stability is to release two protons and two neutrons in the form of a helium nucleus, , ---16.1 The Nucleus and Radioactivity + + +, -Chapter 16 Nuclear Chemistry. neutrons-+, --16.
nuclides. Clearly, a key factor in determining stability is the N / Z ratio. The nuclides form a narrow band of stability: very few stable nuclides exist with N / Z < 1 for light nuclide (Z ≤ 10), N / Z ≈ 1 The N / Z ratio of stable nuclides gradually increases as Z increases with N / Z = 1.15 for 6 : 9 :Fe, N / Z = 1.28 for 8 ;Ag

Concept #2: non-radioactive isotopes with the optimum number of neutrons to protons will lie within the valley of stability, while radioactive isotopes will lie outside of it.
Activity Worksheets, Math Worksheet, Worksheets For Free, Blank Worksheet Template, Preschool Math Worksheets Free, Free Math Money Worksheets, Free Worksheets For 4th Grade, Free Printable High School Worksheets, 2 Grade Math Worksheet, Time Study Worksheet, Free Math Subtraction Worksheets, Common Core Math Worksheet, Free Math Multiplication ...


















0 Response to "39 band of stability worksheet"
Post a Comment