38 section 11.2 from dna to protein worksheet answers
Protein Synthesis Review Sheets with Keys.pdf Date Class Reinforcement and Study Guide Section 11.2 From DNA to Proteih Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. 1. strand of nucleotides 2. sugar 3. nitrogenous base In your textbook, read about the genetic code. Complete each statement. 4. Proteins are made up of 5. There are twenty different types of 6. AP Biology 2017-2018 - Mrs. Paul Read and take notes (on a separate piece of paper) Ch 12.1-12.3, write a summary for each section; DNA Reading with Questions and Coloring; 11/16 Due 11/17: Watch the Bozeman Videos for DNA and RNA (Take 1 and Take 2) and answer the study questions; Create a Venn Diagram to compare and contrast DNA and RNA; 11/17 Due 11/20: DNA Extraction Post Lab
Section 43 46 what are the characteristics of z dna Section: 4.3 46) What are the characteristics of Z-DNA and what does the Z in Z-DNA stand for? Ans: Z-DNA is a double helix that is left-handed, in contrast with the right-handed screw sense of the B-DNA helix. The phosphates in the backbone zigzag; hence, the name Z-DNA.
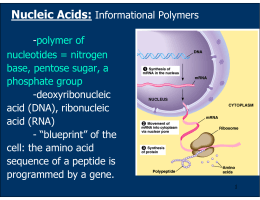
Section 11.2 from dna to protein worksheet answers
DOC Chapter 11 Multiple Choice Practice Test - New Century Academy a. binding induces changes in the cells that lead to cell fusion. b. the cells then produce the a factor and the factor. c. one cell nucleus binds the mating factors and produces a new nucleus in the opposite cell. d. the cell membranes fall apart, releasing the mating factors that lead to new yeast cells. e. FINAL: Chapter 11.2 From DNA to Protein Flashcards - Quizlet in transcription enzymes unzip a section of DNA to be copied. Free RNA nucleotides form ___ pairs with their __ nucleotides on the DNA. base; complementary. the mRNA strand breaks away the DNA strands ___ ... DNA, RNA, protein synthesis - Dabdoub. 47 terms. Chapter 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis. 33 terms. RNA and Protein Synthesis. 91 terms ... Essential Biology 11.2 Muscles and Movement AHL - SlideShare 2. Outline the antagonistic nature of the action of muscles in the human body, using the elbow as an example. 3. Flexing (bending)ExtendingBicepsTriceps. 4. Compare the action of the hip and knee joints. 5. Hip (similar to shoulder)KneeType of jointBall and socketRange of movementBonesLeverFemurFlex/ effortExtend/ effortImage. 6.
Section 11.2 from dna to protein worksheet answers. Science 9 2011 - Mrs N. Nelson's Science Website Science 9 - 2011. May 23 to June 11/12. Review For Sc 9 Exam. Summarize key ideas page 68/69. Know vocabulary page 68/69. Redo question 1-21 page70/71. Summarize key ideas page 102/103. Know vocabulary page 102/103. 11.2 From DNA to Protein Section. 11.2 From DNA to Protein. North Carolina Objectives Objective 3.01 Analyze the molecular basis of heredity including: Protein synthesis.6 pages Biology - MY SITE - Weebly Chapter 2: Glencoe Virtual pH lab. Lab 3: Virtual Macro-molecule Lab . Enzyme Action Lab Directions. Enzyme Action Lab Report Template. Chapter 2 Vocabulary Review Part A (Terms 1-22) Chapter 2 Lab: Enzyme Action (RESULTS INPUT) Bozeman Science Video: Atoms and Molecules. Chapter 2 Vocabulary Review Part B (Terms 23-41) Video: Protein Structure. Biology Chapter 11 - DNA - AWS Section 11.2 From DNA to Protein and. DNA. Class is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. RNA.. are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. for the same amino acid.8 pages
kkh00116 CH11.indd Page 304 8/18/08 12:44:03 PM newuserh00116 CH11.indd ... In this chapter's activities, you will (1) learn how to determine whether a stain is blood, (2) characterize simulated blood according to the ABO/Rh system, and (3) learn what information investigators can obtain from bloodstain patterns. No human blood is used in any of the activities. Blood at the Scene of the Crime Reminder Biology 11.1 - phhscience.weebly.com Chapter 11-2 Chapter 11-3 Chapter 12 Chapter 12-1 Chapter 12-2 ... DNA, RNA, and Protein Formation Series of Videos DNA Lecture 18 Things you should know about genetics What is DNA. DNA Structure. DNA Song DNA Replication Lab DNA Extraction Section 11.1 Quiz Direction for making model Paper for model DNA Lab. DNA Starter Activity: File Size ... PDF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY AND APPLIED GENETICS - Carter Center it was DNA that carried the genetic information. 1953-Franklin and Wilkins study DNA by X-ray crystallography which subsequently lead to unrevealing the double helical structure of DNA by Watson and Crick 1960s- Smith demonstrate that the DNA can be cleaved by restriction enzymes DP Biology: Quizzes tests & revision - ThinkIB Quizzes tests & revision. Quizzes tests & revision. There is no getting away from assessment. This page leads to a range of resources to help teachers and students to review and revise the understandings and skills set out in the IB guide. There are many resources for reviewing knowledge and understanding on this site.
Biology 2010 Student Edition - GradeSaver Chapter 11, Introduction to Genetics - Assessment - 11.2 Applying Medel's Principles - Understand Key Concepts/Think Critically - Page 332: 8 Answer c. Work Step by Step The physical characteristics that are displayed in an individual is that individual's phenotype. Genetics is the study of heredity, the passing down of traits to descendants. PDF Chapter Pacing Guide - glencoe.com •Teach the main concepts of Section 11.2. •Have students complete the Critical Thinking/Problem Solving worksheet in small groups. In-Class Check •Have students read the BioLab, follow the Procedure, and answer the Analyze and Conclude questions •Assess students' answers to the BioLab, and discuss their results. PDF CK-12 Biology Quizzes and 11. Science cannot answer all questions. a.The above statement is true because science cannot answer matters of belief. b.The above statement is true because all science is based on logic. c.The above statement is false because science can prove that life evolves over time. PPTX DNA is the only molecule that changes the phenotype ... - KSU | Faculty Web Students will be able to a.) describe the molecular structure of DNA and RNA and indicate similarities and differences; b.) understand the internal structure of DNA strands and how DNA complementary pairing arises Necessary for future material on:
9.3 Transcription - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition To do this, the DNA is "read" or transcribed into an mRNA molecule. The mRNA then provides the code to form a protein by a process called translation. Through the processes of transcription and translation, a protein is built with a specific sequence of amino acids that was originally encoded in the DNA.
Ch. 11 Multiple Choice - Microbiology - OpenStax RNA to DNA to protein DNA to protein to RNA 3. Which of the following is the enzyme that replaces the RNA nucleotides in a primer with DNA nucleotides? DNA polymerase III DNA polymerase I primase helicase 4. Which of the following is not involved in the initiation of replication? ligase DNA gyrase single-stranded binding protein primase 5.
Section 11.2: From DNA to Protein Flashcards - Quizlet Start studying Section 11.2: From DNA to Protein. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Home. ... 15 answers. QUESTION. how does a ribosome know what protein to make? 6 answers. ... Ch 11.2 Worksheet. 16 terms. WD55. DNA/RNA Whole Unit. 28 terms. Christina_Isaac. Chapter 13 BIO Quiz. 37 terms.
DNA review Packet KEY to study .pdf Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms an important part of both subunits of the ribosomes, the cell structures where proteins are assembled. ▻Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries ...14 pages
Topic 2.7: DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Rule - one base always pairs with another is called complementary base pairing.This makes sure that the two DNA molecules that are created by DNA replication are identical in their base sequences to the parent molecule that was replicated. 2.7.U2 Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the two strands by breaking hydrogen bonds.
Chapter12 packet - SlideShare DNA polymerase is an enzyme that joins individual nucleotides to produce a new strand of DNA. During replication, DNA may be lost from the tips of chromosomes, which are called telomeres. 6. Replication in Living CellsThe cells of most prokaryotes have a single, circular DNA molecule in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells have much more DNA.
Core Bio DNA Review Answers.pdf - Georgetown ISD In your textbook, read about genes and proteins and RNA. Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure. DNA.3 pages
10.1 Cloning and Genetic Engineering - Concepts of Biology - 1st ... Biotechnology is the use of artificial methods to modify the genetic material of living organisms or cells to produce novel compounds or to perform new functions. Biotechnology has been used for improving livestock and crops since the beginning of agriculture through selective breeding. Since the discovery of the structure of DNA in 1953, and ...
Transcription and Translation - Cell Biology, Genetics, and ... 11.2 Protein Translation Translation is the process by which mRNAs are converted into protein products through the interactions of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. Even before an mRNA is translated, a cell must invest energy to build each of its ribosomes, a complex macromolecule composed of structural and catalytic rRNAs, and many distinct polypeptides.
InThinking DP Biology Plenty of links, worksheets and interactive resources that support the new IB course. Sarah Jackson, Diocesan School for Girls, New Zealand. If you are looking for a reliable source to help you plan and teach the new IBDP Biology course, this website is a must. Mandy Watson, Berlin International School, Germany.
Protein Synthesis Reading Essentials.pdf Section. 11.2 From DNA to Protein. SC.F.1.4.1 The student knows that the body processes involve specific biochemical reactions governed by biochemical ...21 pages
11.2 DNA Replication - Microbiology | OpenStax 11.2 DNA Replication - Microbiology | OpenStax Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the meaning of semiconservative DNA replication Explain why DNA replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand Explain why Okazaki fragments are formed
Solved: Chapter 17 Problem 16ECP Solution - Chegg Access Practical Business Math Procedures with Handbook, Student DVD, and WSJ insert 11th Edition Chapter 17 Problem 16ECP solution now. Our solutions are written by Chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!
Biology 2010 Student Edition - GradeSaver Chapter 11, Introduction to Genetics - 11.1 - The Work of Gregor Mendel - 11.1 Assessment - Page 312: 1c Answer Segregation means that during gamete formation, the alleles of each of the genes separate from one another; therefore, each gamete carries a single allele for each gene. Work Step by Step
PPTX 11.1 The Work of Gregor Mendel Key Questions - Weebly 11.1The Work of GregorMendel Mendel studied traits that had just 2 alleles, one dominant and one recessive. The allele for tall plants was dominant and the allele for short plants was recessive. However, most traits involve much more complicated patterns of inheritance. DOMINANT ALLELES - CAPITAL LETTERS recessive alleles - lower case letters A
DOCX PC\|MAC What is the name of the molecule that completes the flow of information from DNA to protein? How are the nitrogen bases of RNA different from DNA? List two other ways in which RNA is different from DNA. When you finish your notes, complete this diagram comparing DNA and RNA. RNA DNA DNA and RNA Structure Comparison Double Strand Single Strand














0 Response to "38 section 11.2 from dna to protein worksheet answers"
Post a Comment