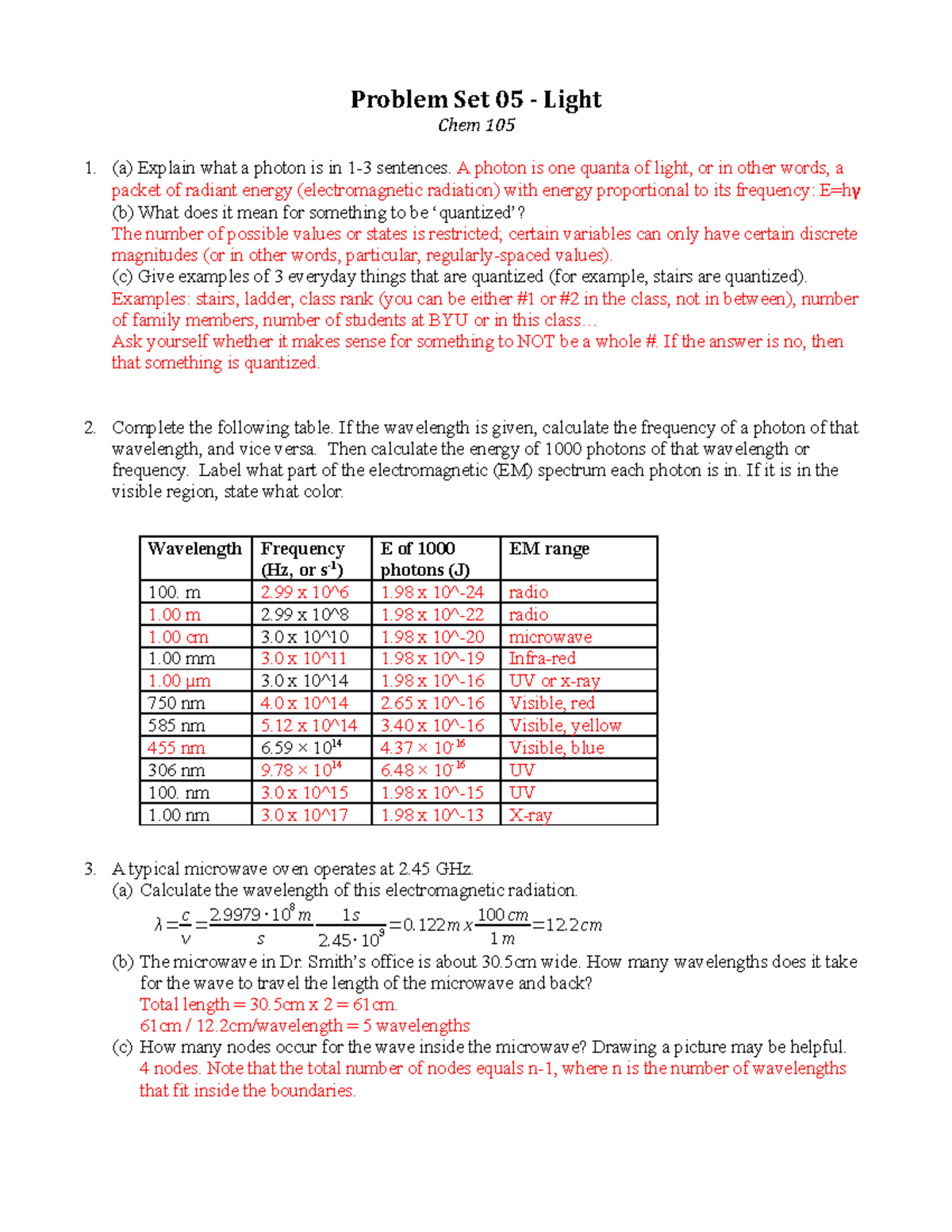
41 12.2 chemical calculations worksheet answers
Chapter 12 wanted quantity and Gis the given quantity. The values of aand bare the coefficients from the balanced equation. • The general solution for a mole-mole problem is given by xmol G = mol W bmol W xb amol G a Writing and Using Mole Ratios 12.2 Chemical Calculations > Bookmark File PDF Unit 9 Stoichiometry Crossword Chapter Packet Answers Chemical Reactions Chapter 12 Study Guide (Unit 9) 2 | P a g e 12.2 Chemical Calculations In chemical calculations, mole ratios are used to convert between moles of reactant and moles of prod-uct, or between moles of products. In a typical stoichiometric problem, the given quantity (starting quantity) is first converted to moles.
Chapter 12 - Stoichiometry - 12.2 Chemical Calculations - Sample ... Chapter 12 - Stoichiometry - 12.2 Chemical Calculations - Sample Problem 12.6 - Page 396: 17 Answer 1.93 L O2 Work Step by Step The volume of one mole of gas at STP is 22.4 L. Use this as a conversion factor. Use molar mass and/or mole ratio in order to convert the units into the desired quantities. Update this answer!

12.2 chemical calculations worksheet answers
PDF CHAPTER 12 Study Guide - Quia 12.2 Chemical Calculations 39. Explain the term mole ratioin your own words. When would you use this term? 40. Carbon disulfide is an important industrial sol- vent. It is prepared by the reaction of coke with sulfur dioxide. 5C(s) 2SO 2 (g)¡CS 2 (l) 4CO(g) a. How many moles of CS 2form when 2.7 mol C reacts? b. Chapter 122 Chemical Calculations Answers - tunxis.commnet.edu Chemical Calculations Worksheet Answers CHAPTER 2 REVIEW Measurements and Calculations SECTION 2 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Complete the following conversions: a. 100 mL 0.1 L b. 0.25 g 25 cg c. 400 cm3 0.4 L d. 400 cm 3 0.0004 m 2. For each measuring device shown PDF A Guide to Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Change Four basic steps need to be followed to solve this type of calculation. The steps are 1. Balance the equation. 2. Convert the amounts of a given substance to moles. 3. Using the mole ratio, calculate the moles of substance yielded by the reaction. 4. Convert moles of the required substance back to the desired quantity.
12.2 chemical calculations worksheet answers. 12.2 Chemical Calculations Flashcards | Quizlet 12.2 Chemical Calculations STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity mole ratio Click card to see definition 👆 A conversion factor derived from the coefficients of a balanced chemical equation interpreted in terms of moles. Click again to see term 👆 1/2 Created by abooth13 Terms in this set (2) mole ratio PDF Worksheet 4.1 Mole calculations calculation of amounts of substances that may take part in chemical reactions. Various formulas are used to calculate the amount of substance (in mol): n = m M, where n = number of mol and M = molar mass (g mol-1) n = L N, where N 23= number of particles and L = Avogadro's constant (6.02 10 mol-1) No. Question Answer 1 Calculate the ... PDF Ksp and Molar Solubility Problems Worksheet - troy.k12.oh.us explanation / calculations to support answer. 8. A volume of 75 mL of 0.060 M NaF is mixed with 25 mL of 0.15 M Sr(NO3)2. Calculate the concentrations in the final solution of NO3‐, Na+, Sr2+, and F‐. (K sp for SrF2 = 20.x10 ‐10) 12.4 Integrated Rate Laws - Chemistry | OpenStax The Half-Life of a Reaction. The half-life of a reaction (t 1/2) is the time required for one-half of a given amount of reactant to be consumed. In each succeeding half-life, half of the remaining concentration of the reactant is consumed. Using the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (Figure 12.2) as an example, we find that during the first half-life (from 0.00 hours to 6.00 hours), the ...
12.1 The Arithmetic of Equations 12.2 Chemical Calculations 12.3 ... 12.1 The Arithmetic of Equations 12.2 Chemical Calculations 12.3 Limiting Reagent and Percent Yield STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity The coefficients of a balanced chemical equation indicate the relative number of _____ of reactants and products Click card to see definition 👆 Moles Click again to see term 👆 1/25 12.2 Exothermic and endothermic reactions | Energy and chemical change ... In an endothermic reaction, Δ H is greater than zero because the energy of the reactants is less than the energy of the products. Energy is absorbed in the reaction. For example: C (s) + H 2 O (ℓ) → CO (g) + H 2 (g) Δ H > 0. Some of the information relating to exothermic and endothermic reactions is summarised in Table 12.1. Mole Calculations Review Worksheet - answers on next page. - SharpSchool 1. Calculate the molar mass of each compound. a. LiOH c. Mg(C 2H 3O 2) 2 b. barium bromide d. Ca(NO 3) 2 2. How many molecules are in 45.0 grams CH 4? 3. How many moles are in 18.8 grams NaOH? 4. A salt 23shaker containing 9.58 x 10 formula units NaCl contains how many moles? 5. Which of the following has the greatest mass? 4.2 moles C PDF Chemical Reactions Chapter 12 Study Guide (Unit 9) 12.2 Chemical Calculations In chemical calculations, mole ratios are used to convert between moles of reactant and moles of product, or between moles of products. In a typical stoichiometric problem, the given quantity (starting quantity) is first converted to moles.
PDF CK-12 Chemistry •Answer the Check Your Understanding questions. •Answer/reflect on the Points to Consider questions. •Write additional questions about an upcoming lesson, chapter, or unit of study. •Draw pictures of living organisms and diagrams of life processes. •Take notes and define academic vocabulary. CK-12 Chemistry Worksheet Name _____ Class _____ Date _____ Answer each of the questions below to show your achievement of the lesson objectives. Lesson Objective: Define chemistry. 1.Chemistry is the study of a.living systems b.the stars and planets c.all matter d.reactions in a test tube Online Library Chapter 12 Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS Chapter 12 Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer www2.dusd.net www2.dusd.net Chapter 10 - moles (handouts) Chapter 11 - reactions (handouts) Chapter 12 - stoichiometry (hand- outs) Chapter 13 - states of matter (handouts) Chapter 17 - thermochemistry (handouts) Chapter PDF SECTION 12.1 THE ARITHMETIC OF EQUATIONS - Weebly Use Figure 12.3 on page 357. Complete the table about the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen. 12. Circle the letter(s) of the items that are ALWAYS conserved in every chemical reaction. a.volume of gasesd.moles b.masse.molecules c.formula unitsf.atoms 13. What reactant combines with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide?
Unit 9: Handouts, Reviews, and Answer Keys - PiersonHChem Unit 8: Mole & Chemical Composition. 8.2: % Composition. 8.3: Converting with Moles. 8.4: Molecular + Empirical Formulas. Unit 8: Handouts, Reviews + Answer Keys. Honors Chemistry: Semester 1 Final. ... Answer Keys; Selection File type icon File name Description Size Revision Time User;
PDF Acids and Bases Packet Name: Mods: - VOORHEES SCIENCE WORKSHEET 8 (NOTES) The pH of a WEAK acid solution Calculate the pH of a 0.500 M aqueous solution of formic acid, HCOOH [K a =1.77 x 10-4] Step 1 List the major species in the solution. Step 2 Choose the species that can produce H+, and write balanced equations for the reactions producing H+. Step 3
Answer Keys - HONORS CHEMISTRY Percent Yield Calculations Percent Yield Lab SG 12.3 & 12.4 Chapter 12 Review Quiz 12.3 Chapter 15 Solubility Worksheet SG 15.1 & 15.2 Understanding Molarity Diluting Solutions Molality & Percent Solution Solubility Curve Lab Electrolytes Lab SG 15.3 & 15.4 Reviewing Vocabulary Understanding Main Ideas Chapter 15 Review Chapter 17 & 18 ...
Online Library 122 Chemical Calculations Worksheet Answer Key Just invest little get older to entry this on-line proclamation 122 Chemical Calculations Worksheet Answer Key as well as evaluation them wherever you are now. YP3OSV - LACI LONG The goal of CTD is to provide broad chemical-disease associations published in the literature 92. Concurrently, CTD does not subset
Answer Key Chapter 12 - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax Chapter 12 Chapter 12 1. The instantaneous rate is the rate of a reaction at any particular point in time, a period of time that is so short that the concentrations of reactants and products change by a negligible amount. The initial rate is the instantaneous rate of reaction as it starts (as product just begins to form).
Quia - Class Page - Chem 722 Worksheet 10.1- No Answers . Worksheet 10.1-Key. Mole Conversion Powerpoint. Worksheet 10.2- No Answers. Worksheet 10.2- Key. Percent Composition Powerpoint. Worksheet 10.3- No Answers . Worksheet 10.3- Key . Empirical Formula Lab Write Up-Print To Turn in Tuesday 2/4/14. In Class Review Problems for Ch. 10. In Class Review Problems for Ch. 10- Key
Answer Key Chapter 2 - Chemistry: Atoms First 2e | OpenStax The net charge of such a neutral atom is zero, and the mass number is 12. (c) The preceding answers are correct. (d) The atom will be stable since C-12 is a stable isotope of carbon. (e) The preceding answer is correct. Other answers for this exercise are possible if a different element of isotope is chosen.
PDF CK-12 Chemistry 33.Some scientists study the chemical processes that take place in the sun. Is this pure or applied chemistry? Explain your answer. 34.Why are some people concerned about using nuclear power plants to generate electricity? Answer Key 1.d 2.b 3.c 4.b 5.b 6.d 7.b 8.c 9.c 10.d 11.true 12.false 13.false 14.true 15.true 16.false 17.true 18.true 19 ...
12.2 Chemical Calculations Flashcards | Quizlet Terms in this set (12) AT. In mass- mass calculations, the molar mass is used to convert mass to moles. NT. The mole ratio 2 mol HF/1 molSnF2 can be used to determine the mass of SnF2 produced according to the equation: Sn (s)+ 2HF (g)= SnF2 (s)+H2 (g) AT. In a volume- volume problem, the 22.4L/mol factors always cancel out.
Chapter 12 - Stoichiometry - 12.2 Chemical Calculations - GradeSaver Chapter 12 - Stoichiometry - 12.2 Chemical Calculations - Sample Problem 12.3 - Page 391: 11 Answer 7.4 mol Al Work Step by Step List the six possible mole ratios of the chemical equation. Choose the mole ratio to convert the number of moles of Al2O3 into moles of Al Update this answer!
PDF A Guide to Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Change Four basic steps need to be followed to solve this type of calculation. The steps are 1. Balance the equation. 2. Convert the amounts of a given substance to moles. 3. Using the mole ratio, calculate the moles of substance yielded by the reaction. 4. Convert moles of the required substance back to the desired quantity.
Chapter 122 Chemical Calculations Answers - tunxis.commnet.edu Chemical Calculations Worksheet Answers CHAPTER 2 REVIEW Measurements and Calculations SECTION 2 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Complete the following conversions: a. 100 mL 0.1 L b. 0.25 g 25 cg c. 400 cm3 0.4 L d. 400 cm 3 0.0004 m 2. For each measuring device shown
PDF CHAPTER 12 Study Guide - Quia 12.2 Chemical Calculations 39. Explain the term mole ratioin your own words. When would you use this term? 40. Carbon disulfide is an important industrial sol- vent. It is prepared by the reaction of coke with sulfur dioxide. 5C(s) 2SO 2 (g)¡CS 2 (l) 4CO(g) a. How many moles of CS 2form when 2.7 mol C reacts? b.



























0 Response to "41 12.2 chemical calculations worksheet answers"
Post a Comment